What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D are called three steroid compounds with anti-rickets properties. These are: Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2), 25-hydroxycholecalciferol.
The human body synthesizes vitamin D3 from provitamin present in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
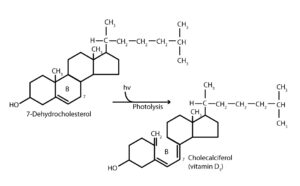
The active form of Vitamin D is transferred to various organs – mostly to the liver – where it is deposited in amounts sufficient even for several weeks. Some is stored in adipose tissue.
Absorption of vitamin D from food products takes place in the small intestine in the presence of bile acids, fatty acids and triglycerides. From there, it is transported into the bloodstream.
Both vitamin D, formed in the skin and absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, enters the liver, where it becomes the main form of vitamin D, which, when combined with protein, enters the kidneys. Here it transforms into the most hormonally active form. This form affects the absorption of calcium in the intestine, is involved in the release of calcium from the bones, and increases its concentration in the blood.
Vitamin D3 functions:
- Necessary for the functioning of the skeletal system, enhances the resorption of calcium and phosphates in the intestines, necessary for the transport of calcium
- It affects the management of phosphates by the kidneys, and thus the development and mineralization of bone tissue
- Strengthens the immune system.
- It affects the secretion of parathyroid hormone produced by the parathyroid glands
Deficiency of Vitamin D3
Proper nutrition with dairy products and sufficient sun exposure to the skin is the best way to prevent vitamin D3 deficiency, which causes:
- Rickets in infants and children
- In adults, especially in pregnant and lactating women, decalcification, softening of the bones (osteomalacia)
- In the elderly, osteoporosis – demineralization, skeletal deformity, sagging, porosity and fragility of the skeletal system
- It also prevents calcium from being completely absorbed from food
Overdosage of Vitamin D3
Although rare, it is very dangerous and leads to intoxication of the body. Such hypervitaminosis causes malaise, anorexia, fatigue, headache, abdominal pain, constipation in children, and diarrhea in adults. It causes irreversible changes and disturbances in the work of the heart, kidney stones.
The demand for Vitamin D3
It depends on the amount produced in the skin under the influence of sunlight, age, diet, calcium and phosphorus content and their mutual proportion. Vitamin D standards are not given for adults, with the exception of elderly people who suffer from poor absorption and reduced production by the body. People over 60 years of age are recommended to take 10 µg of this vitamin daily.
Role during the coronavirus pandemic
A study of the relationship between vitamin D and coronavirus infection, published in October, was conducted by researchers from the University of Birmingham among employees of the NHS working at the University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust. The researchers analyzed blood samples from 392 employees of the facility. They were collected in May, at the end of the first “outbreak” of the epidemic. The blood was tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies – proteins that indicate that the person had built up an immune response during a previous infection. Vitamin D levels were also checked. The results show that among people with vitamin D deficiency, 72% tested positive for coronavirus antibodies, which indicates a previous infection. Among people who did not lack vitamin D, such a result was confirmed in 51 percent.
These results therefore suggest that lower vitamin D levels may increase your susceptibility to COVID-19.
The study also found that hospital workers diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency reported pain symptoms more frequently. Lower vitamin D levels were also observed among people reporting fever (not those who complained of cough or shortness of breath).
In turn, researchers from Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla in Spain found that as many as 80% of the 216 COVID-19 patients admitted between March 10 and March 31 were deficient in vitamin D, with men having lower vitamin D levels than women.
Of the 216 hospitalized, 19 patients – who had been taking oral vitamin D supplements for more than three months prior to admission – were analyzed as a separate group.
Researchers reported a higher incidence of vitamin D deficiency in hospitalized COVID-19 patients compared to the control group. However, they found no association between vitamin D levels and disease severity, such as the need for ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, a group of hospitalized patients who took vitamin D supplements prior to admission to the hospital had slightly better results than those who did not take them.
Short summary
As one of the co-authors of the above – mentioned studies well said, given the safety and low cost of vitamin D treatment, it would be wise to administer it to those who are most likely to be deficient – such as seniors and people with comorbidities – as well as those who have also the highest risk of developing COVID-19 and severe consequences of the disease.
Sources:
Helena Ciborowska, Anna Rudincka, Dietetyka. Żywienie zdrowego i chorego człowieka, Wyd. 3 uzupełnione, Warszawa, PZWL, 2007, ISBN 978-83-200-3254-3
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-8814521/Having-vitamin-D-deficiency-make-likely-catch-Covid-19-study-claims.html
https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/university/colleges/mds/news/2020/10/vitamin-d-covid.aspx
https://www.gazetaprawna.pl/artykuly/1494721,witamina-d-a-zakazenie-koronawirusem-ciekawe-badania-hiszpanskich-naukowcow.html